- Surgery
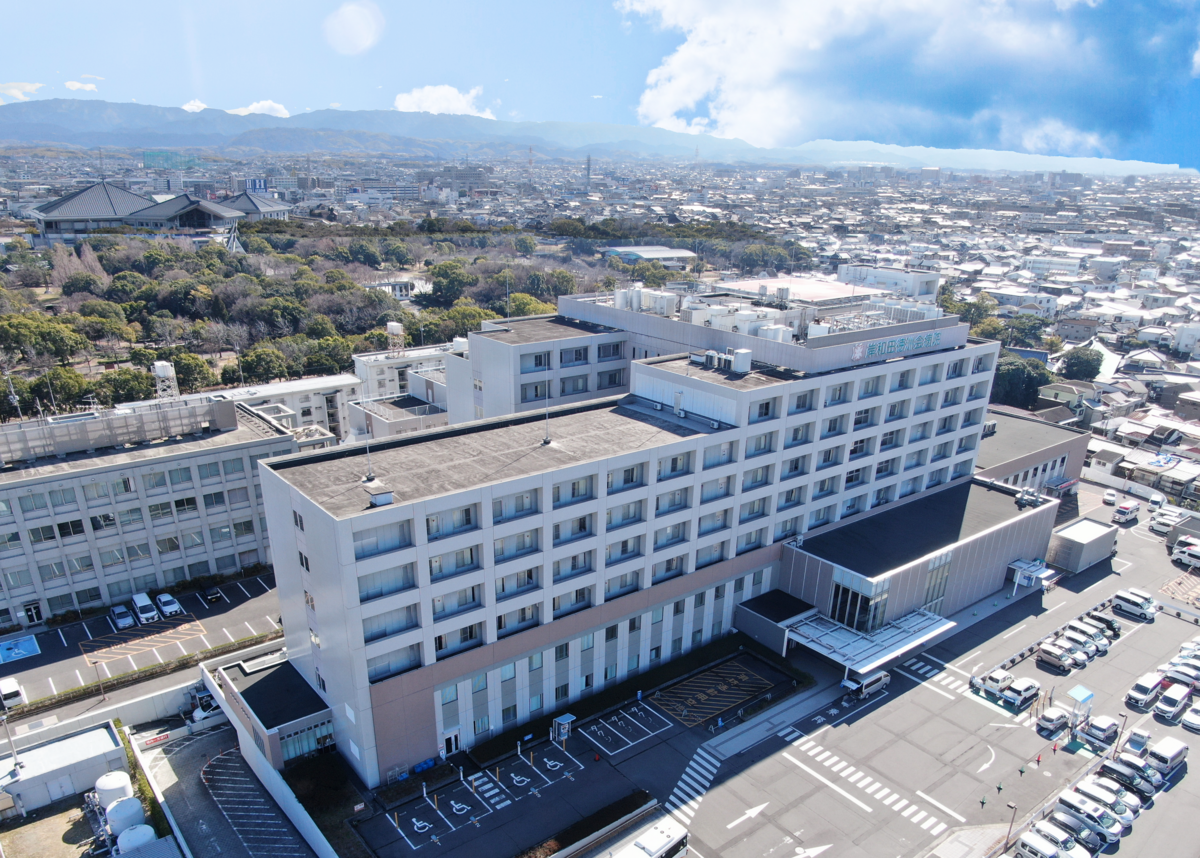
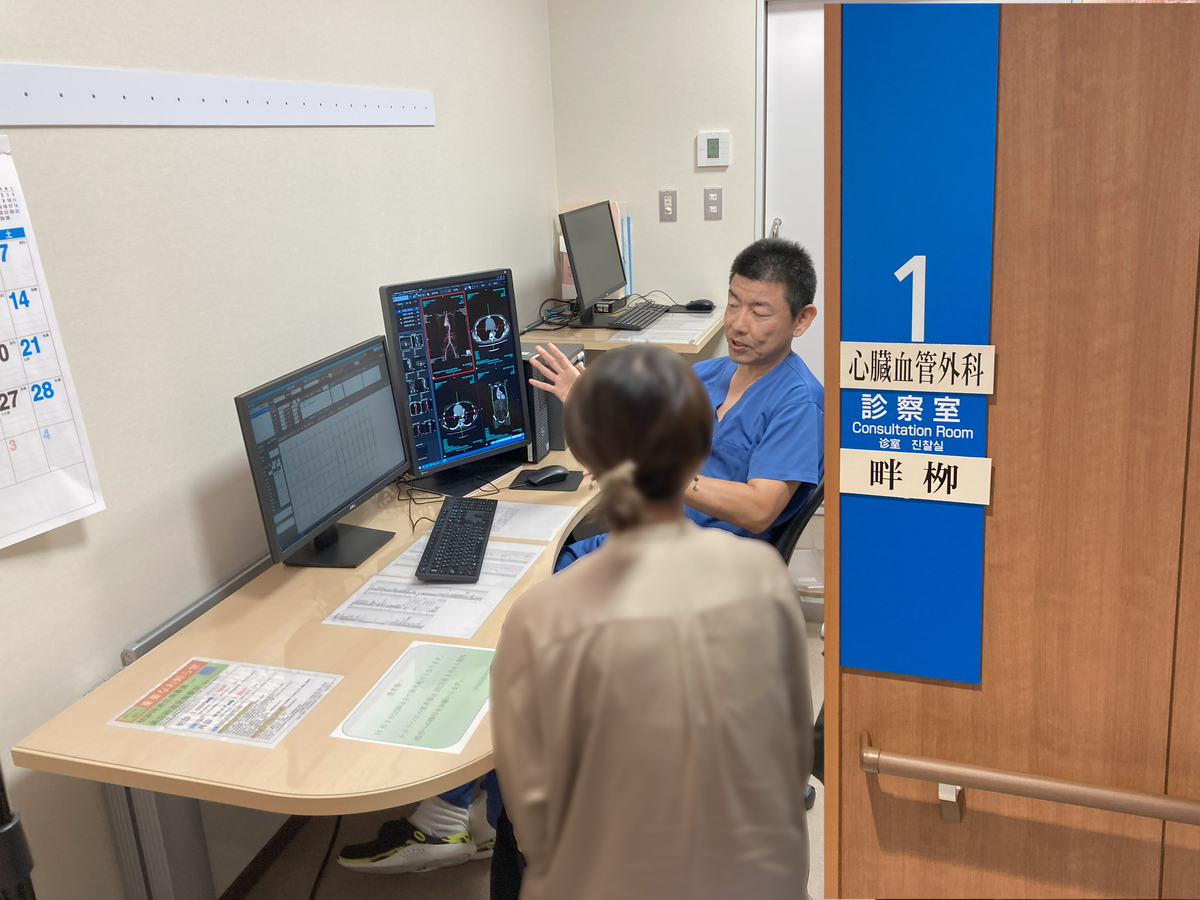
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Treatment 【Kishiwada Tokushukai Hospital】





for more information about this program,
please contact us here
please contact us here
other program on this facility